Today we will talk about the most famous landmarks of the world affected by fires. Some of them could not be replenished, others had rebelled like a phoenix.
"Water Lilies" by Claude Monet
This picture and its owners had no luck from the very beginning. One of the late works of impressionist Claude Monet, which depicts the peaceful expanse of the pond and flowering lilies, went through several fires and gained mystical glory. Almost immediately after the canvas was finished, the workshop of the artist himself caught fire. The picture did not suffer and later decorated the cabaret in Montmartre, but not for long - after a few weeks it burned to the ground. Miraculously preserved "Water Lilies" acquired the French collector Otto Schmidz. A year later, such a fire broke out in his house that only one wall remained of the building - the one on which the infamous masterpiece hung. The Museum of Modern Art in New York in 1957 risked buying it. But a year later, on the second floor, flames flared. On that day, an air conditioner was installed in the building, and during the break, workers smoked in cans of paint, sawdust and cloth, which covered the canvases. Presumably, this led to a fire. This time the lilies did not manage to get out of the fire unharmed: the five-meter canvas was completely lost, and little work from the same series suffered greatly. She tried to recover within three years, but to no avail. An employee of the museum died in the fire, several firefighters suffered from carbon monoxide poisoning.
Assumption Church in Kondopoga
One of the most beautiful wooden churches of the 18th century died in fire last August: only ashes remained from the Assumption Church on the shore of Lake Onega in Kondopoga. The monument of architecture of Zaonezhsky which survived the Soviet years completely burned out in just three hours. The fire broke out inside and quickly swept the 42-meter structure - one of the highest in Russia. The fire destroyed the last authentic interior of wooden churches in Russia: the five-tier baroque iconostasis and the iconic ceiling-sky with the composition Divine Liturgy, restored in 2006. The “sky” was divided into 16 faces, in each of which an angel was depicted, in the center - the image of Christ, in the corners - the holy evangelists. The last church service was held in 2015, the next three years the museum of local lore was working in the room. According to the main version, the cause of the tragedy was the careless handling of tourists with fire. Karelian officials claim that the hipped temple can be restored.
National Museum of Brazil
The three-storey palace of San Cristovan in Rio de Janeiro caught fire in September 2018. It housed the National Museum of Brazil: of the 20 million exhibits, only a few were saved. The fire started in the evening, after closing, so there were no casualties. 80 firefighters extinguished the fire until the morning: the hydrants were out of order, and they had to go to get to the nearest lake to get water. The flames destroyed large paleontological and archaeological collections, ancient Egyptian artifacts, Greek and Roman sculptures. You can no longer see the 12,000-year-old skeleton of a woman in South America and the dinosaur skeleton. The fire did not survive the largest meteorite that fell in Brazil, and the fresco from Pompeii, which survived the eruption of Vesuvius. These and other invaluable exhibits scientists collected over 200 years. Now the museum is undergoing restoration work.
Moscow Manege
Manege stood in the center of Moscow for almost 200 years: a covered parade ground for military parades and parades was built after the fire of 1812 on the site of a burnt-out wooden building according to a unique project of Spanish engineer Augustine Betancourt. The huge building without columns survived three revolutions and two wars, but in March 2004 a fire broke out here. The wooden structures of the ancient structure flashed instantly. After half an hour, almost the entire roof was burning, the flame rose to a height of 50 m and in an hour covered an area of 2000 m2. The fire burned from nine in the evening until two in the morning: by the morning of March 15, only the walls remained.
The fire was given the highest category of complexity, it was extinguished by more than 60 fire brigades. During the elimination of emergencies due to the collapse of the roof killed two firefighters, one was seriously injured. Trolleybus wires on Mokhovaya, parked cars and crowds of inquisitive passersby prevented the extinguish of fire. Therefore, they could only localize the fire by midnight, when the building was almost completely burnt out. A year later, the building was restored, adding new underground floors. But the original solid beams of larch replaced with glued, so many architects and art historians called Manege replica.
Namdaemun Gate in Seoul
South Korea lost its main character in February 2008: a strong fire destroyed the ancient Namdaemun gate (Great South Gate) in Seoul. The firefighters arrived at the scene almost immediately, but could not reach the source of the fire: for this they needed to disassemble the roof or wall of the historical monument, and no one decided to do this without the permission of the authorities. While negotiations were underway, the wooden part of the construction of the end of the 14th century burned to the ground. Later it turned out that the 70-year-old Korean had set fire to the Great South Gate. So he decided to take revenge on the authorities who paid him too little compensation for the building of his land. The ancient monument was restored almost five years and opened at the end of 2012. The gates were restored according to old drawings, they worked on the wooden part by hand, and paints for painting were brought from Japan. A large-scale project cost the country $ 22 million.
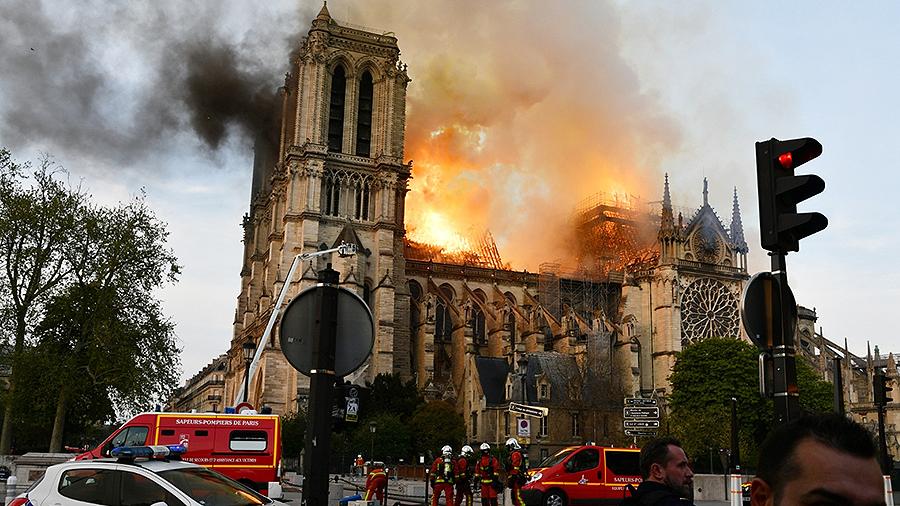
Notre Dame Cathedral
The main Catholic church in Paris and the symbol of the French capital erupted on Holy Monday, the evening of April 15th. The cause of the incident is only establishing, but according to the preliminary version, wooden scaffolding around the church caught fire (restoration work was going on in the cathedral). During the fire the roof, the spire and the clock collapsed, the supporting structures and the left tower burned, but the complete collapse of the building was prevented. All night, 400 firefighters were extinguished by Notre Dame de Paris, and only by the morning of April 16 were they able to contain the fire. From the island of Cité, on which the temple stands, all residents and tourists were evacuated. Parisians were on their knees, crying and praying. According to French media reports, one of the firefighters and two policemen were seriously injured in the course of fire fighting.
Some of the relics were saved: some paintings and statues, an altar, an altar cross and the main shrine of Notre Dame — the crown of thorns of Jesus Christ — were not injured. He was kept in a special safe: it saved him from fire. But the degree of preservation of stained glass windows, three bodies and the bell is not yet known. French President Emmanuel Macron announced that the cathedral would be restored. According to preliminary estimates of experts, it may take up to several decades. Immediately after the fire, the state fund for the preservation of the cultural heritage of France began to raise funds for the restoration of the temple. During the first day they collected more than half a billion euros.